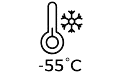News & Events
Why Class II is required for home healthcare applications?
12
Aug
Aug 12, 2022

The emerging needs of home healthcare
Population aging is the global phenomenon resulting from the decreasing birth rate and increasing life expectancy in many countries. It could be expected that the elderly may have higher chances to deal with chronic diseases. Therefore, in addition to hospital care, some basic treatments and monitoring could be done at home and in the places such as nursing homes for the elderly with chronic diseases. Home healthcare is usually less expensive and more convenient and could be an ideal option for the elderly. For example, oxygen saturation measurement and ventilators are commonly seen in private houses and nursing homes.
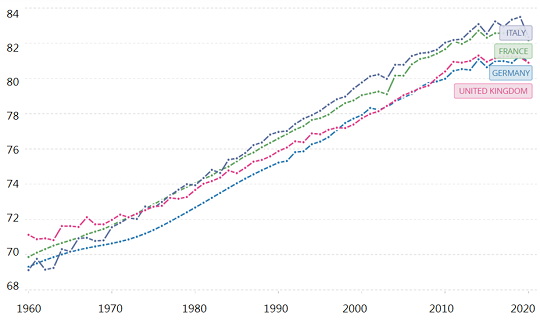
Fig.1 Life Expectancy from World Bank's Statistics
In fact, medical equipment needs to meet the strict requirements for home healthcare environment. The IEC 60601-1-11 defines requirements for the essential performance of medical equipment and systems. Moreover, it also needs to be compliant to the strict electromagnetic compatibility requirements according to the IEC 60601-1-2 4th Edition in home healthcare environment.
Here are several points showing the IEC 60601-1-11 safety requirements and indicating key restrictions on home healthcare medical equipment:
1.Ambient conditions (storage temperature at -25 to 70 °C and operating temperature at 5 to 40 °C with 93% RH)
2.Class II protection (NO protective earth connection is permitted).
3.Enclosure protection against water and dust must be at least IP21 (light rain); trasit-operatable, handheld and body-worn equipment must be at least IP22.
4.Stronger shock and vibration tests (30 min random vibration test per axis)
5.Low mains supply requirements are broader:
-15% of minimum rated voltage
-20% of minimum rated voltage for life supporting equipment
What is Class II protection?
The IEC 61140 standard classifies electrical appliances into several protection classes which are Class I, Class II, and III. Let’s see the differences among them below:
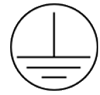
Fig.2 Class I symbol
Class I appliances protect users from hazardous AC input voltage by providing two levels of protection which are basic insulation and a grounded conductive case (the earth connection).
Class I appliances are usually made of metal, and three cables, a metal earth pin and a fuse in the plug are also included. By connecting the metal parts to the earth (ground) wire, it would let the metal parts maintain the state of the electrical potential of earth. When the live or neutral wire touch the metal case/parts, there will be a fault in the circuit. In the case, the earth wire of Class I appliances will direct the current into the ground and then a fuse will blow either in the plug or the main fuse box in order to protect end users.
One way to check if it is Class I is to look for the Class I symbol on the device. Examples of Class I products are coffee machines, toasters, microwaves, and kettles.
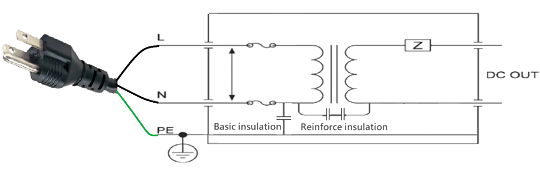
Fig.3 Typical protection Class I
Fig.4 Class II symbol
The following figure shows typical Class II protection. Class II power supplies of the appliances offer users two layers of protection against hazardous input voltage via a basic insulation plus a supplemental insulation or a reinforced insulation. A Class II product usually has a plastic chassis. One way to identify a Class II product is to look for the Class II symbol on the label. Examples of Class II products are TVs, photocopiers, computers.
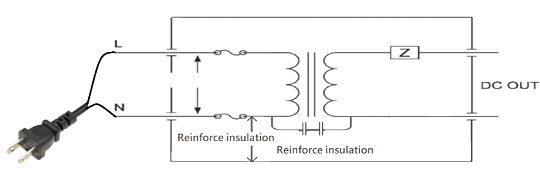
Fig.5 Typical protection Class II
Fig.6 Class III symbol
Class III appliances are designed to be supplied from a safety isolating transformer. The transformer must have two separate windings called the “Primary Winding”, which is connected to the input, and the “Secondary Winding”, which is connected to the output. The output is known as Separated Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) or ES1 limit shown in the following table. It must not exceed 30 VAC or 60 VDC and is normally below 24 VDC or 12 VDC. Examples of Class III products are laptops, smart phones.
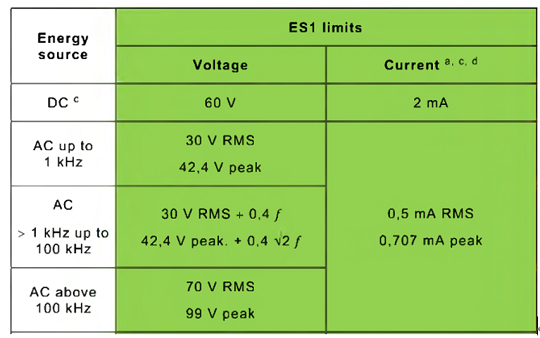
Fig.7 ES1 Table
Why Class II is important for household and homehealth care?
The background of this requirement lies in the fact that many buildings in USA and Europe have no proper grounding or even no grounding. In many old houses, it is common to use the metal water pipes as the grounding electrode. However, there is one problem often seen in these old houses that the plumbing systems were fixed and replaced with cheap plastic pipes or loose clamps. As the result, it may possibly cause the safety issue that these houses have no proper grounding now.
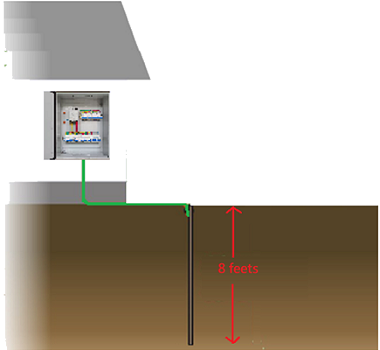
Fig.8 correct grounding method
Under this circumstance, for a Class I appliance, a current flows to the earth through the protective conductor during the occurrence of fault and then it activates the residual current circuit device or a fuse. It may lead to an electrical shock or an increased leakage current. Also, it could become a hazard to the users or patients if there is no grounding or no proper grounding such as the one shown in Fig.8 above.
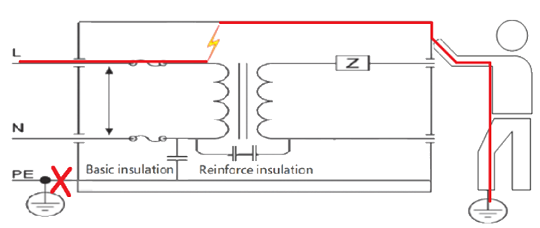
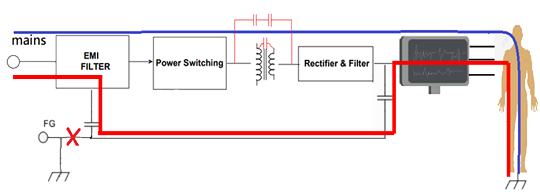
Based on this reason, the class II power supplies in appliances would be a better choice because they have two layers of protection including the basic and the supplenmental or reiforced insulation to effectively reduce the risk of electrical shock.
Conclusion
Due to the trend of population ageing and the deep impact of COVID-19, the demand for home healthcare equipment has increased. For the safety to the users or patients for using home healthcare equipment at home and in nursing homes, Class II power supplies would be the first and only choice. The following list is the Cincon product portfolio for home healthcare power supplies including AC-DC desktop and wall-mount adapters from 18W to 220W.
Medical Class I & Class II Desktop Power Adapters:
| Model | Power | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Leakage Current | Features |
| TR70M | 70W | 80-264 | 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V, 36V, 48V | Touch: 90µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m IEC/EN 60601-1-11 (TR70MB) IP21 |
| TR160M | 160W | 80-264 | 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V | Touch: 90µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m IEC/EN 60601-1-11 (TR160MB) IP22 |
| TR220M | 220W | 80-264 | 12V, 24V, 36V, 48V, 56V | Touch: 100µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m IEC/EN 60601-1-11 (TR220MB) IP22 |
Medical Class II Desktop Power Adapters:
| Model | Power | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Leakage Current | Features |
| TR36M | 36W | 80-264 | 5V, 9V, 12V, 13.5V, 15V, 18V, 24V, 36V, 48V | Touch: 80µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m EN60601-1-11 IP21 |
Medical Class II Wall-mount Adapters with Interchangeable Plugs:
| Model | Power | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Leakage Current | Features |
| TR18RDM | 18W | 80-264 | 5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V | Touch: 30µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m EN60601-1-11 IP22 |
| TR30RDM | 30W | 80-264 | 5V, 9V, 12V, 15V, 18V, 24V | Touch: 50µA (Max) | 2MOPP Altitude 5000m EN60601-1-11 IP22 |
Contact sales@cincon.com.tw for support.